
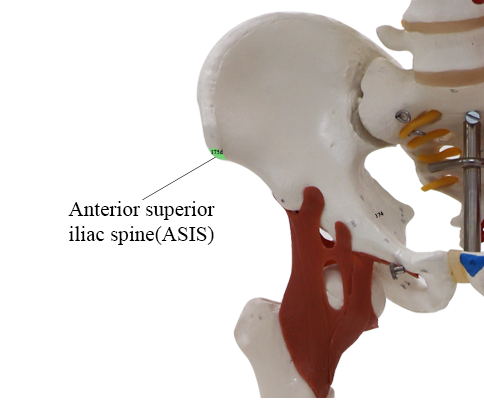
Similarly, physical therapists and chiropractors rely on palpatory diagnostic principles and tests to guide their diagnoses and treatments. The ability to accurately determine symmetry of the ASIS levels is critical because errors in this assessment can lead to inaccurate diagnosis and improper intervention with osteopathic manipulative treatment. The symmetry or asymmetry of the right and left anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) anatomic landmark levels is used to help identify muscle imbalance in the pelvic region and dysfunction of the iliosacral joints, 1, 2(pp14-21), 3(pp238-241), 4(pp228-237), 5(p503) which can contribute to complaints such as low back pain. Various bone landmarks are assessed in this examination. Its physical findings can lead to the diagnosis of somatic dysfunctions that guide patient treatment. The osteopathic structural examination is key to evaluating patients from an osteopathic perspective. This form of assessment can be used to screen for ASIS asymmetry. Length of experience positively influences the percentage of correct results, and eye dominance does not significantly change this outcome. No statistically significant differences were found in the percentage of correct results by eye dominance.Ĭonclusion: Assessment of ASIS is sensitive but not specific at discrepancies of 5 mm or greater. The overall sensitivity was 82.8% (5-mm discrepancy) and 91.7% (10-mm discrepancy), and the specificity was 31.0%. Differences by level of training were statistically significant only for the 5-mm ASIS discrepancy, where participants with more experience performed better. The overall percentages of correct results were 31.0% (even levels), 82.8% (5-mm discrepancy), and 91.7% (10-mm discrepancy). Results: A total of 147 examiners (participants) participated in this study (66 first-year and 61 second-year medical students, 15 fellows, and 5 osteopathic physicians). Dominant and nondominant eyes were used independently to assess ASIS levels. Methods: Osteopathic physicians, predoctoral teaching fellows, and first- and second-year osteopathic medical students from a single teaching institute assessed 3 plastic pelvic models with ASIS anatomic landmarks set at different levels: even and 5- and 10-mm descrepancies. Objective: To assess the influence of homogeneous training, years of experience, and eye dominance on the percentage of correctness, sensitivity, and specificity of ASIS evaluation.

Context: Assessment of the anterior superior iliac spine (ASIS) is a key component in generating the pelvic diagnosis of somatic dysfunction, but studies have shown poor reliability between examiners.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
